What Is the Difference Between a Systematic Review and Meta Analysis
Covidence explains the departure between
systematic review & meta-analysis.
Systematic review and meta-analysis are two terms that you might see used interchangeably. Each term refers to research near research, but in that location are important differences!
A systematic review is a piece of work that asks a research question and then answers it past summarising the prove that meets a set of pre-specified criteria. Some systematic reviews present their results using meta-analysis, a statistical method that combines the results of several trials to generate an average effect. Meta-analysis adds value because it can produce a more precise guess of the effect of a treatment than considering each report individually 🎯.
Let's take a look at a few related questions that you lot might have nearly systematic reviews and meta-analysis.
🙋🏽♂️ What are the stages of a systematic review?
A systematic review starts with a inquiry question and a protocol or research plan. A review team searches for studies to answer the question using a highly sensitive search strategy. The retrieved studies are and then screened for eligibility using the inclusion and exclusion criteria (this is washed past at to the lowest degree two people working independently). Next, the reviewers extract the relevant data and assess the quality of the included studies. Finally, the review team synthesises the extracted report data (mayhap using meta-assay) and presents the results. The process is shown in figure 1.

Covidence helps researchers consummate systematic review quickly and easily! It supports reviewers with study option, data extraction and quality cess. Data exported from Covidence can be saved in Excel for reliable transfer to your choice of data assay software or, if you're writing a Cochrane Review, to RevMan 5.
🙋🏻♀️ What does 'systematic' really mean?
In this context, systematic means that the methods used to search for and analyse the information are
transparent, reproducible and defined before searching begins. This is what differentiates a systematic review from a descriptive review that might be based on, for example, a subset of the literature that the author is familiar with at the time of writing. Systematic reviews strive to be as thorough and rigorous as possible to minimise the bias that would upshot from cherry-picking studies in a non-systematic way. Systematic reviews sit at the peak of the evidence hierarchy because it is widely agreed that studies with rigorous methods are those best able to minimise the chance of bias on the results of the study. This is what makes systematic reviews the most reliable form of evidence (see figure 2).
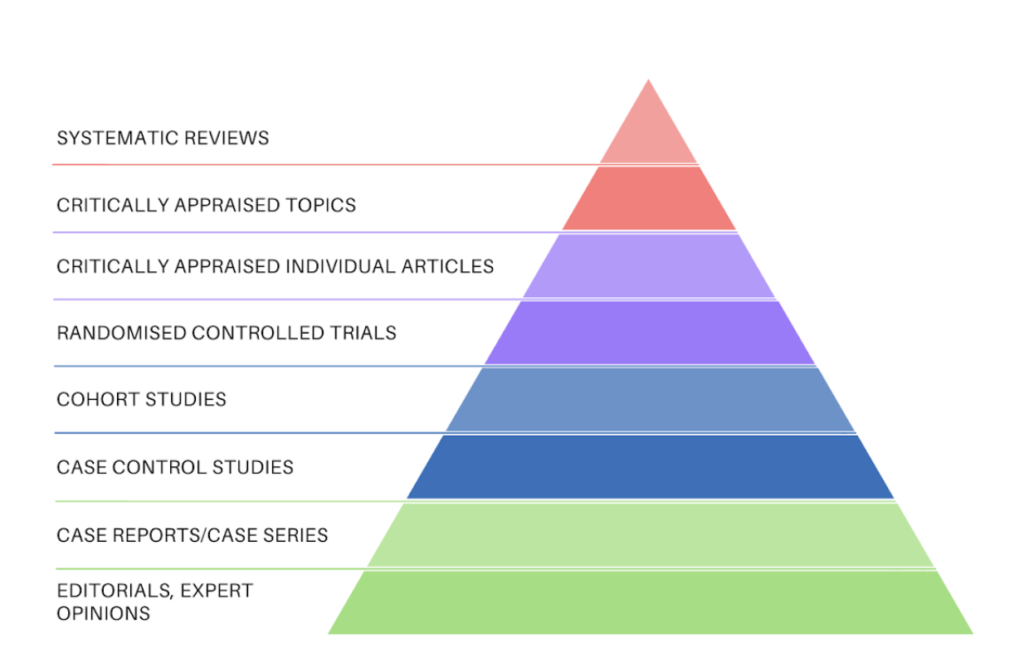

🙋🏾♂️ Why don't all systematic reviews utilize meta-assay?
Meta-analysis can improve the precision of an event guess. But information technology can also be misleading if it is performed with data that are not sufficiently similar, or with data whose methodological quality is poor (for case, because the written report participants were non properly randomized). So it'due south non always appropriate to use meta-analysis and many systematic reviews do not include them. Reviews that practice not contain meta-analysis tin still synthesise study information to produce something that has greater value than the sum of its parts.
🙋🏾♀️ What does meta-analysis do?
Meta-assay produces a more precise estimate of treatment effect. There are several types of effect size and the most suitable blazon is chosen by the review team based on the type of outcomes and interventions nether investigation. Typical consequence sizes in systematic reviews are the odds ratio, the risk ratio, the weighted mean difference and the standardized mean difference. The results of a meta-analysis are displayed using a forest plot like the one in effigy three.
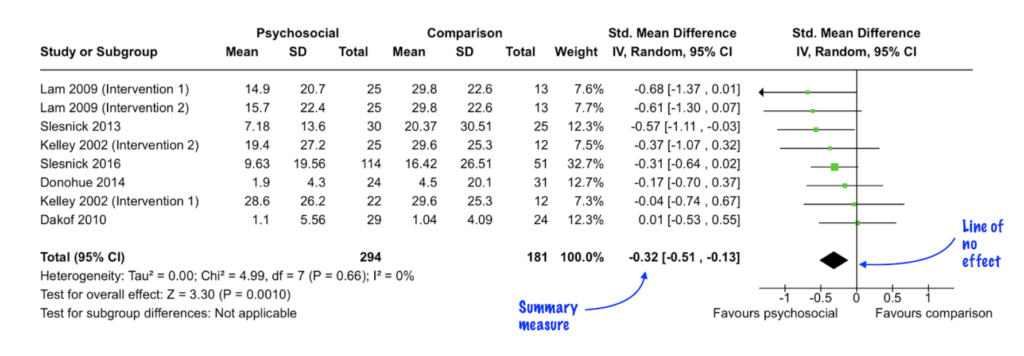
Some meta-analyses also include subgroup assay or meta-regression. These techniques are used to explore a factor (for instance, the age of the written report participant) that might influence the relationship between the treatment and the intervention. Plans to analyse the data using these techniques should be described and justified before looking at the information, ideally at the research plan or protocol stage, to avoid introducing bias. Like meta-analysis, subgroup analysis and meta-regression are advisable just in certain circumstances.
Systematic reviewer pro-tip
Recall advisedly before yous plan subgroup analysis or meta-regression and always ask a methodologist for communication
🙋🏼♀️ What are the other ways to synthesise prove?
Systematic reviews combine report data in a number of ways to attain an overall understanding of the evidence. Meta-analysis is a type of statistical synthesis. Narrative synthesis combines the findings of multiple studies using words. All systematic reviews, including those that use meta-analysis, are probable to incorporate an element of narrative synthesis by summarising in words the evidence included in the review. Just narrative synthesis doesn't just depict the included studies: it also seeks to explain the gathered testify, for case by looking at similarities and differences between the study findings and by exploring possible reasons for those similarities and differences in a systematic mode. Narrative synthesis should not be confused with narrative review, which is a term sometimes used for a not-systematic review of the literature (for instance in a textbook affiliate) where at that place is no systematic try to address issues of bias.
Conclusion
In that location are many types of systematic review. What they all have in common is the use of transparent and reproducible methods that are divers before the search begins. There is no 'all-time' way to synthesise systematic review evidence, and the most suitable approach will depend on factors such equally the nature of the review question, the type of intervention and the outcomes of interest.
Covidence is a web-based tool that saves you time at the screening, option, data extraction and quality assessment stages of your review. Information technology provides piece of cake collaboration across teams and a clear overview of task status, helping y'all to efficiently complete your review. Sign upwardly for a costless trial today! 😀
Source: https://www.covidence.org/blog/the-difference-between-a-systematic-review-and-a-meta-analysis/
0 Response to "What Is the Difference Between a Systematic Review and Meta Analysis"
Post a Comment